Platismatia glauca
Cetraria glauca f. fallax
Cetraria glauca var. tenuisecta
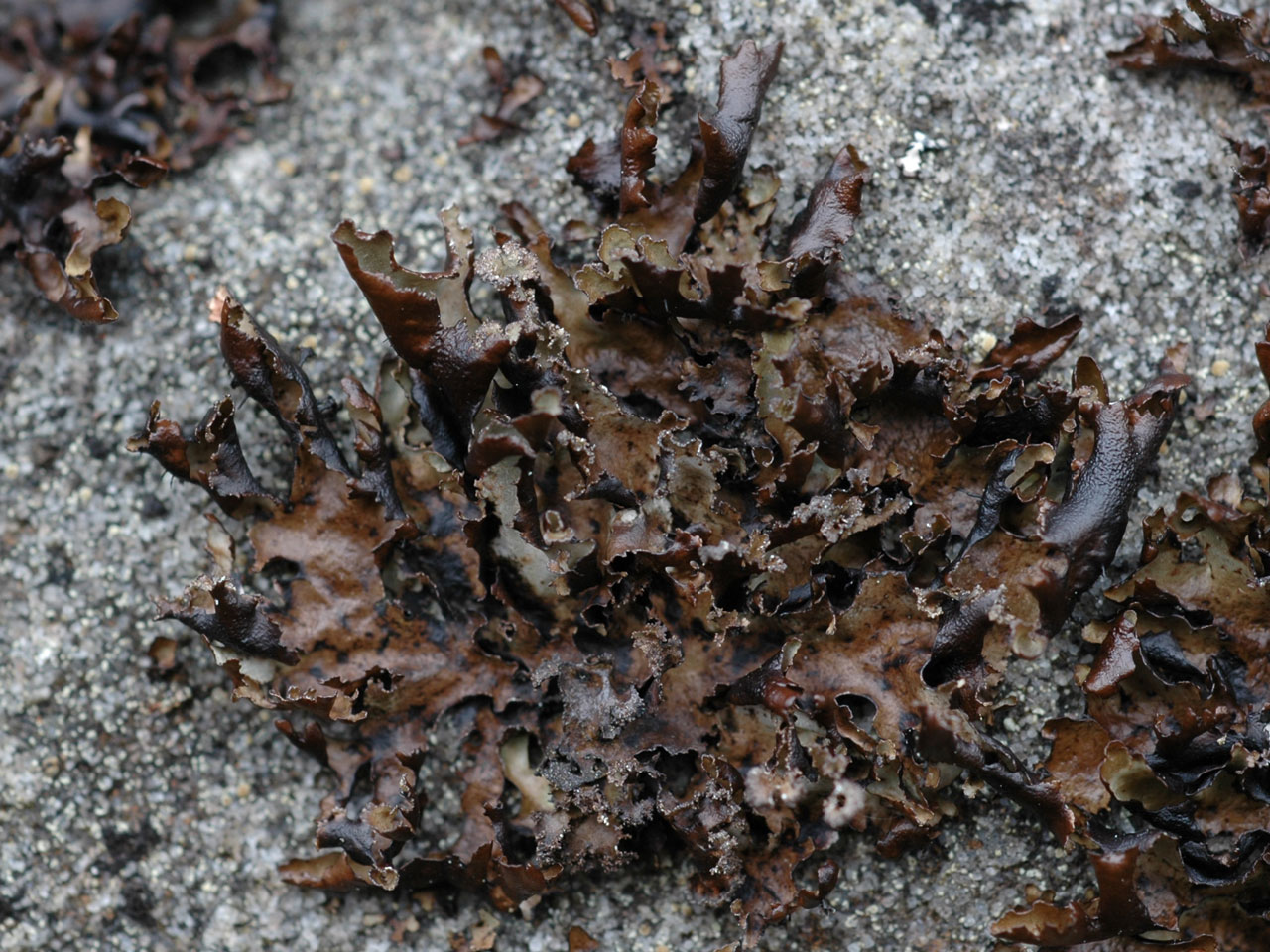
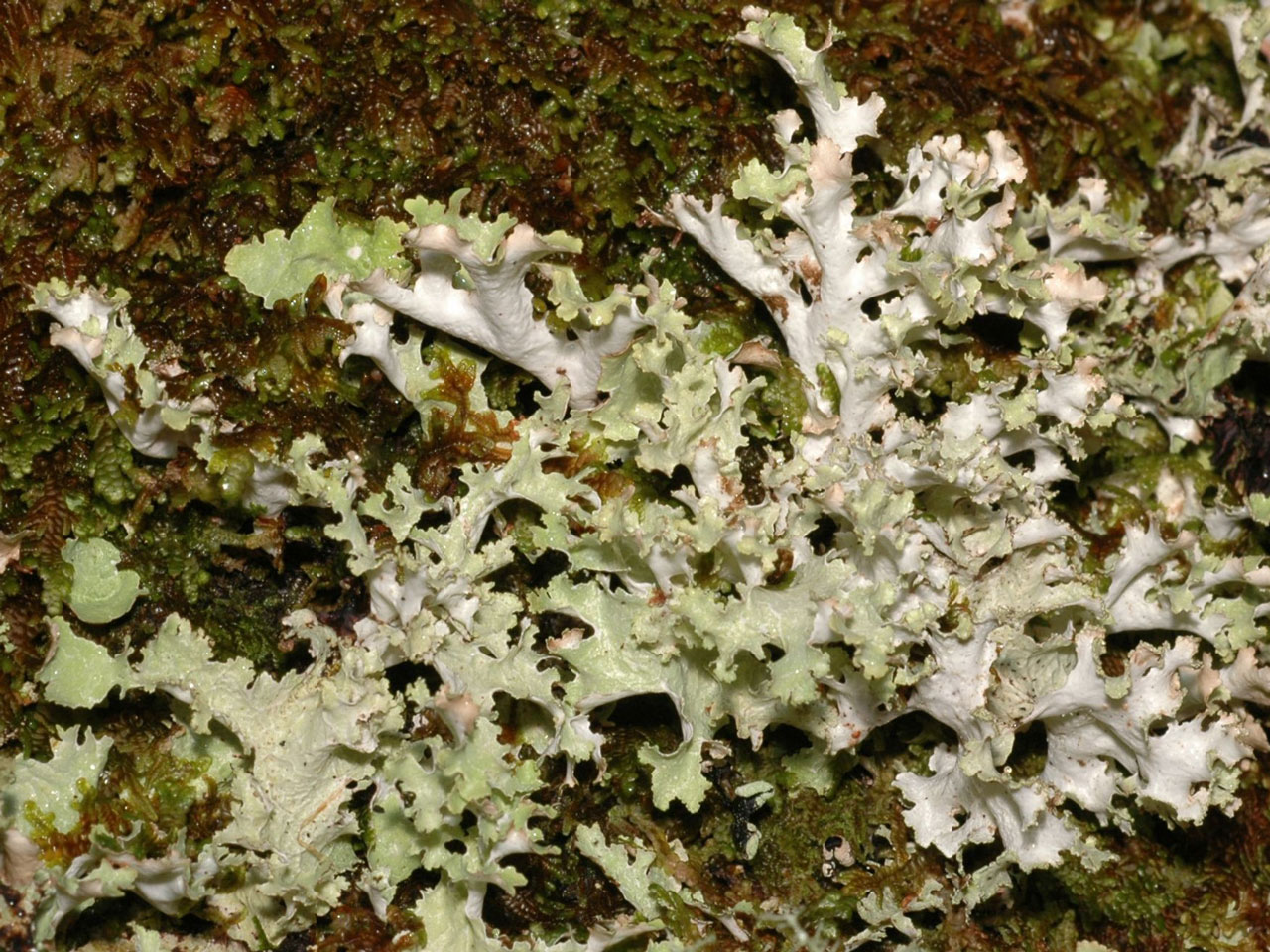
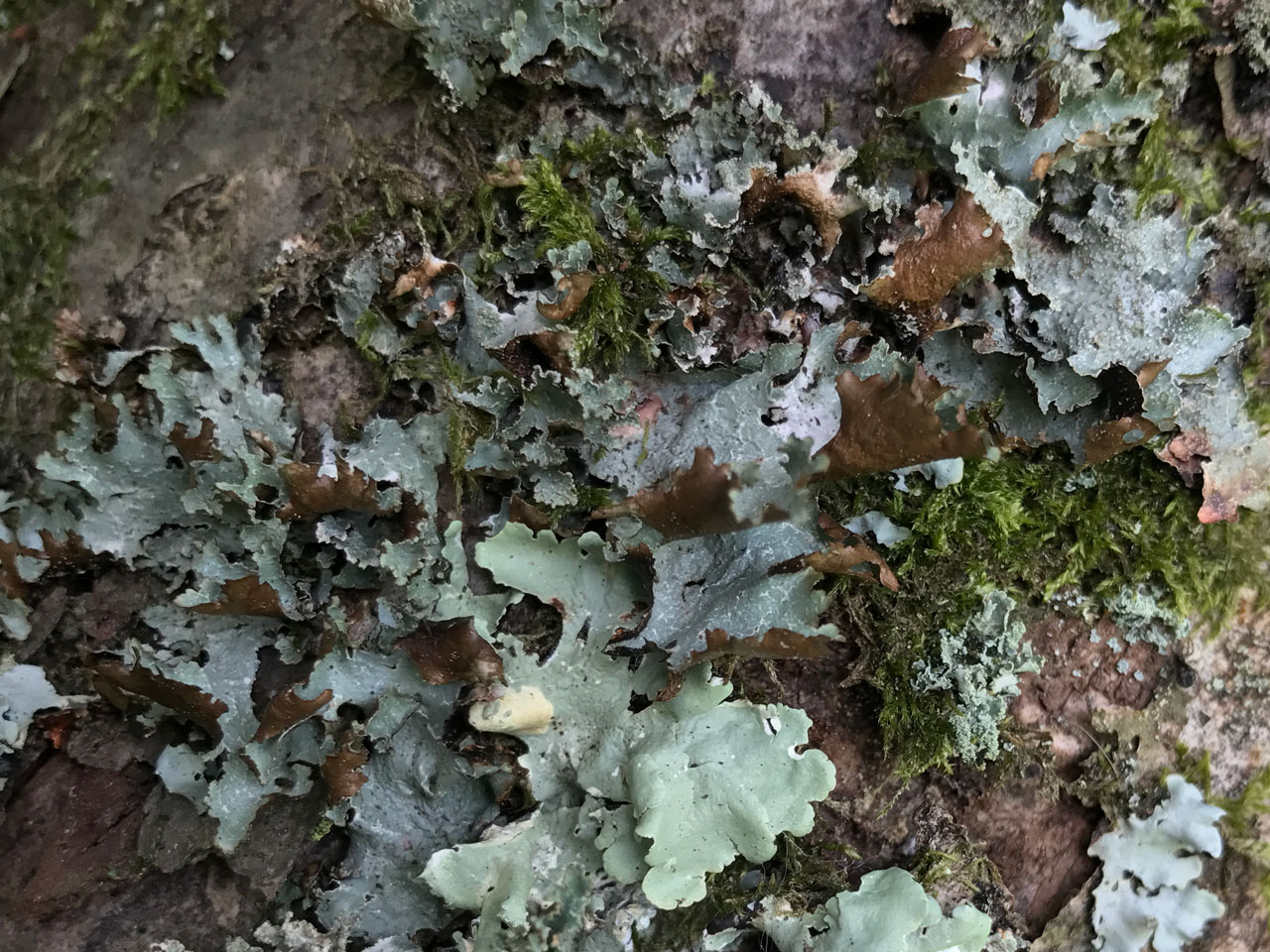
A very variable large leafy lichen with the upper surface pale to dull grey, brownish in exposed sites, and the underside black (brown or white in shade). The wavy and indented lobes give it a characteristic ragged appearance. A species of acid habitats, very common in the uplands but probabaly declining in areas with high levels of ammonia pollution.
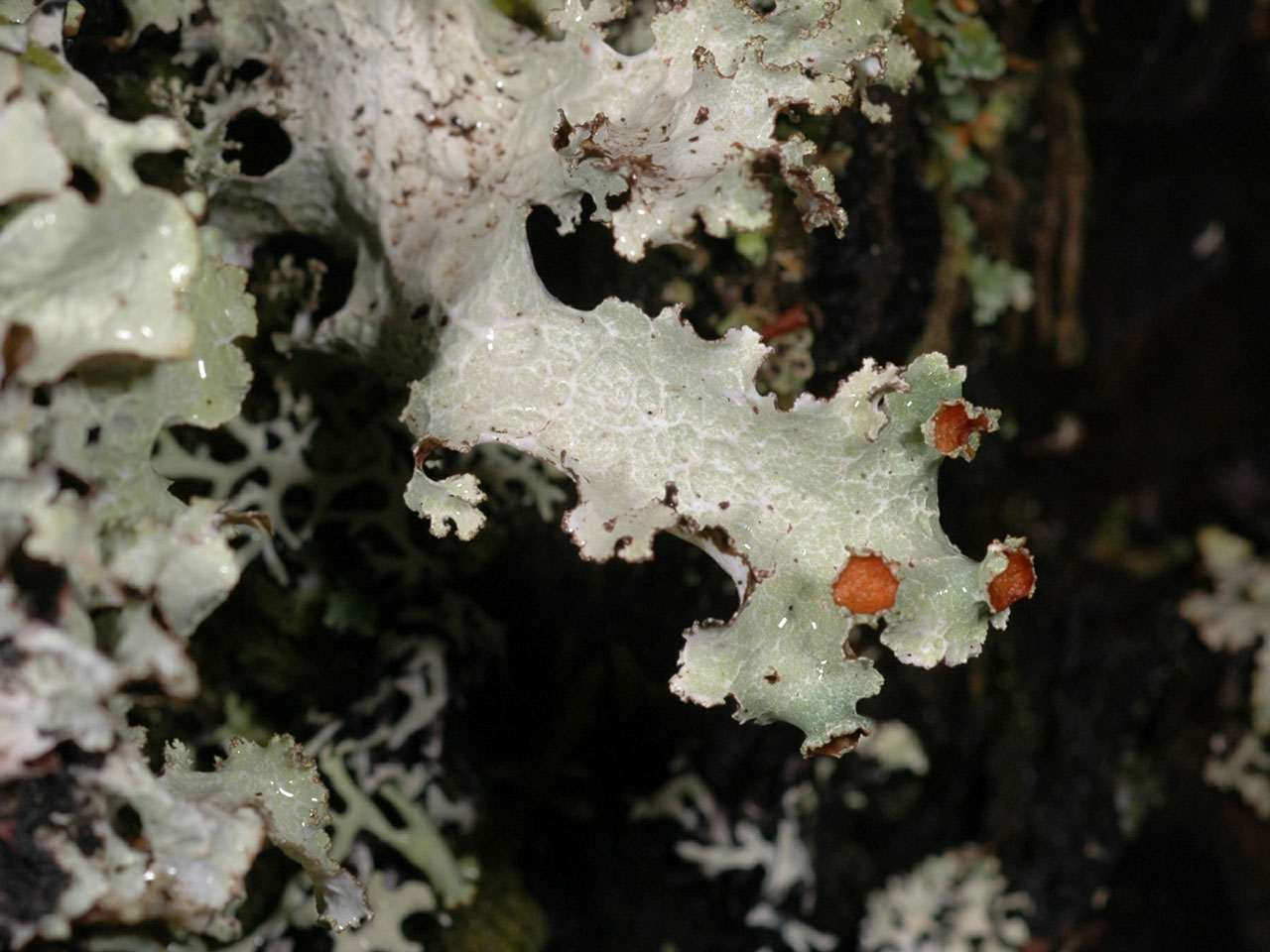
Thallus 1–6 (–15) cm diam, often forming extensive patches, rather thin; lobes to 1.5 cm broad, wavy, irregularly indented, margins ascending, entire or sub-lobulate, often with marginal clusters of simple to coralloid, much branched isidia or (in part) granular soredia; upper surface pale to dull grey, often with a brown tinge or totally tinged brownish in exposed sites, ± unchanged in colour when wet, smooth to wrinkled or slightly ridged, without pseudocyphellae; lower surface entirely black (brown or white in shade), especially towards the margin, with few to many scattered unbranched or branched rhizines. Apothecia very rare, 5–9 mm diam., marginal; disc red-brown; thalline margin thin, ± excluded at maturity. Ascospores 3.5–8.5 × 3–5 μm. Cortex K+ yellow (atranorin), medulla C–, K–, KC–, Pd–, UV– (caperatic acid).
A very variable species; the lobes may be elongate, ± entirely erect with much dissected, coralloid-lobulate- isidiate margins or ± closely adpressed with only the margins upturned with granular-sorediate isidia. The isidia or soredia are mainly confined to the margins but, on occasion, may also occur in small patches or widely dispersed on the upper surface. Tuckermannopsis chlorophylla has brown lobes turning olive-green when wet. Cetrelia olivetorum has scattered, dot-like pseudocyphellae on the upper surface (×10), a C+ pink medulla and finely sorediate margins. See Platismatia norvegica for the distinguishing features of this similar but much rarer northern species.
Phylogenetic analysis of Platismatia glauca sequences reveals two major clades, both of which are represented in our region (Asher et al. 2023). However, these could not be correlated with morphological, chemical or ecological features, and they concluded that recognition of cryptic species was premature.
Infection by Tremella coppinsii Diederich & G. Marson (1988) results in a red discoloration on the thallus. Sometimes with galls caused by Nesolechia oxyspora (Tul.) A. Massal. (1856), often also secondarily infected with Abrothallus cetrariae Kotte (1909).
See also Fungi of Great Britain and Ireland
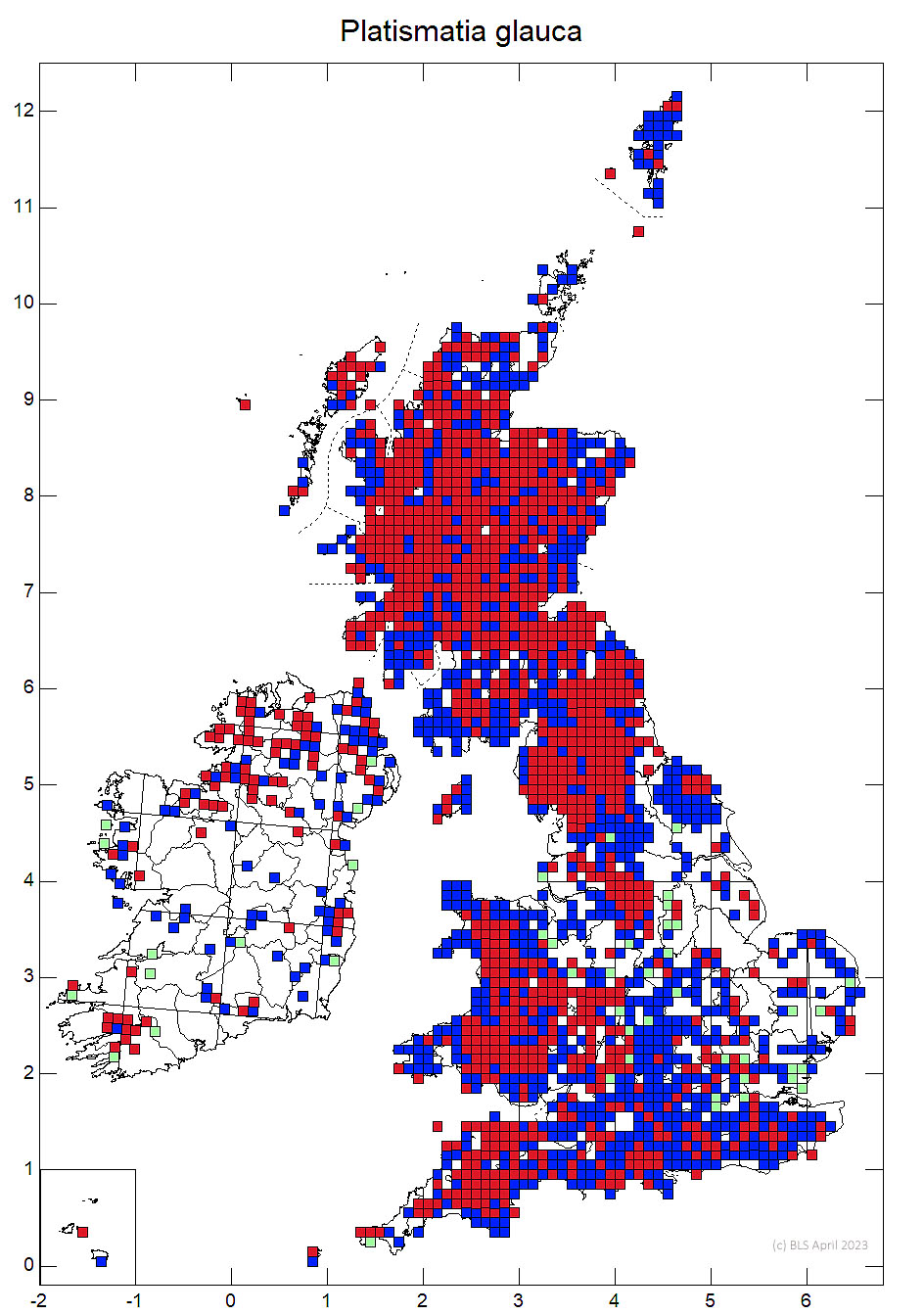
On trees, rocks and soil, especially acidic, leached habitats

Throughout Britain and Ireland, often very common but sharply declining to extinction in areas with high ammonia pollution.
Very sensitive to ammonia pollution and likely to be declining in areas with intensive farming.
Asher, O.A., Howieson, J. & Lendemer, J.C. (2023). A new perspective on the macrolichen genus Platismatia (Parmeliaceae, Ascomycota) based on molecular and phenotypic data. Bryologist 126: 1–18.
Cannon, P., Divakar, P., Yahr, R., Aptroot, A., Clerc, P., Coppins, B., Fryday, A., Sanderson, N. & Simkin, J. (2023). Lecanorales: Parmeliaceae, including the genera Alectoria, Allantoparmelia, Arctoparmelia, Brodoa, Bryoria, Cetraria, Cetrariella, Cetrelia, Cornicularia, Evernia, Flavocetraria, Flavoparmelia, Hypogymnia, Hypotrachyna, Imshaugia, Melanelia, Melanelixia, Melanohalea, Menegazzia, Montanelia, Nesolechia, Parmelia, Parmelina, Parmeliopsis, Parmotrema, Platismatia, Pleurosticta, Protoparmelia, Pseudephebe, Pseudevernia, Punctelia, Raesaenenia, Tuckermannopsis, Usnea, Vulpicida and Xanthoparmelia. Revisions of British and Irish Lichens 33: 1-98.
Text by N A Sanderson, based on Cannon et al (2023).