Cladonia uncialis subsp. uncialis
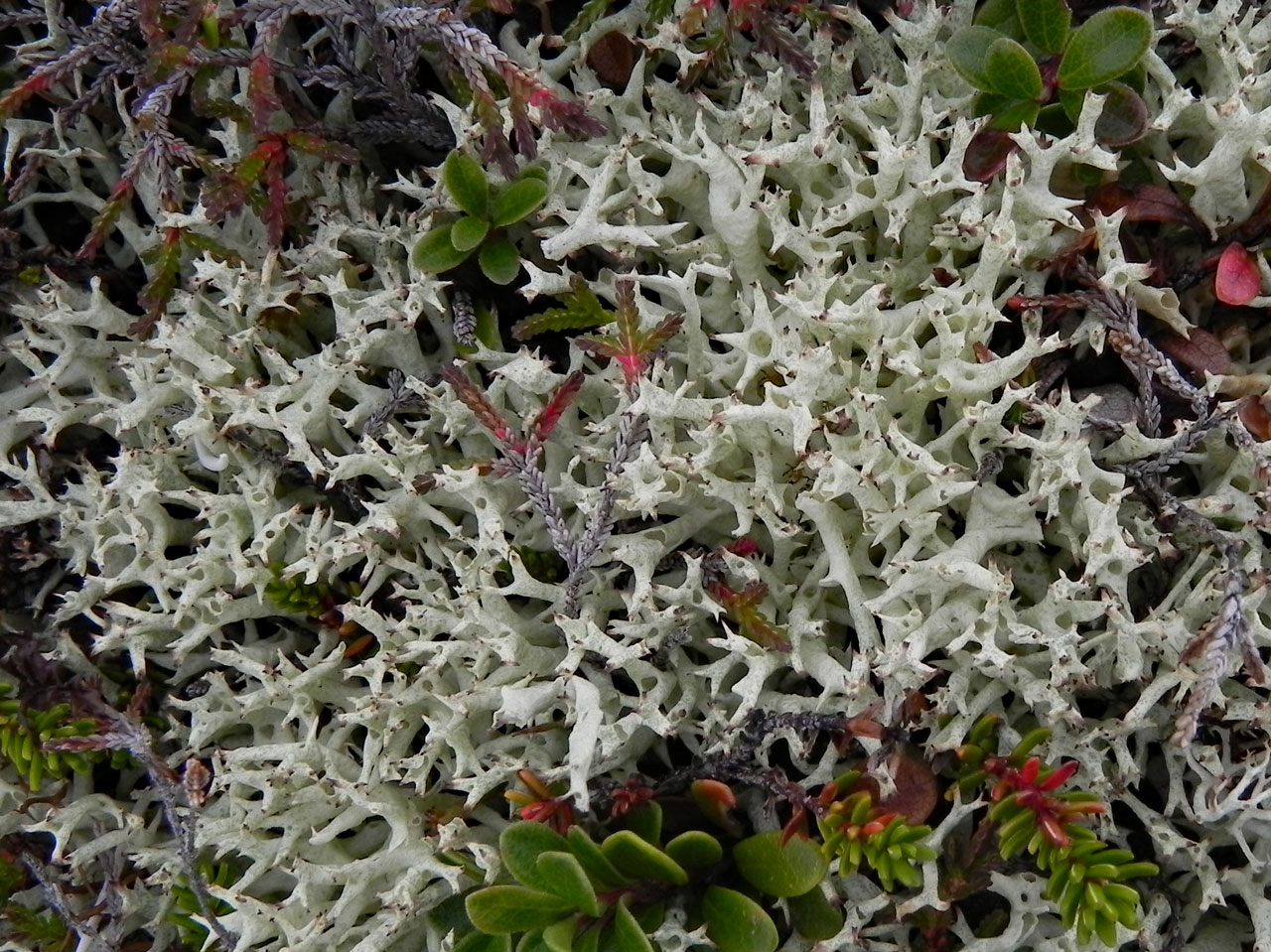
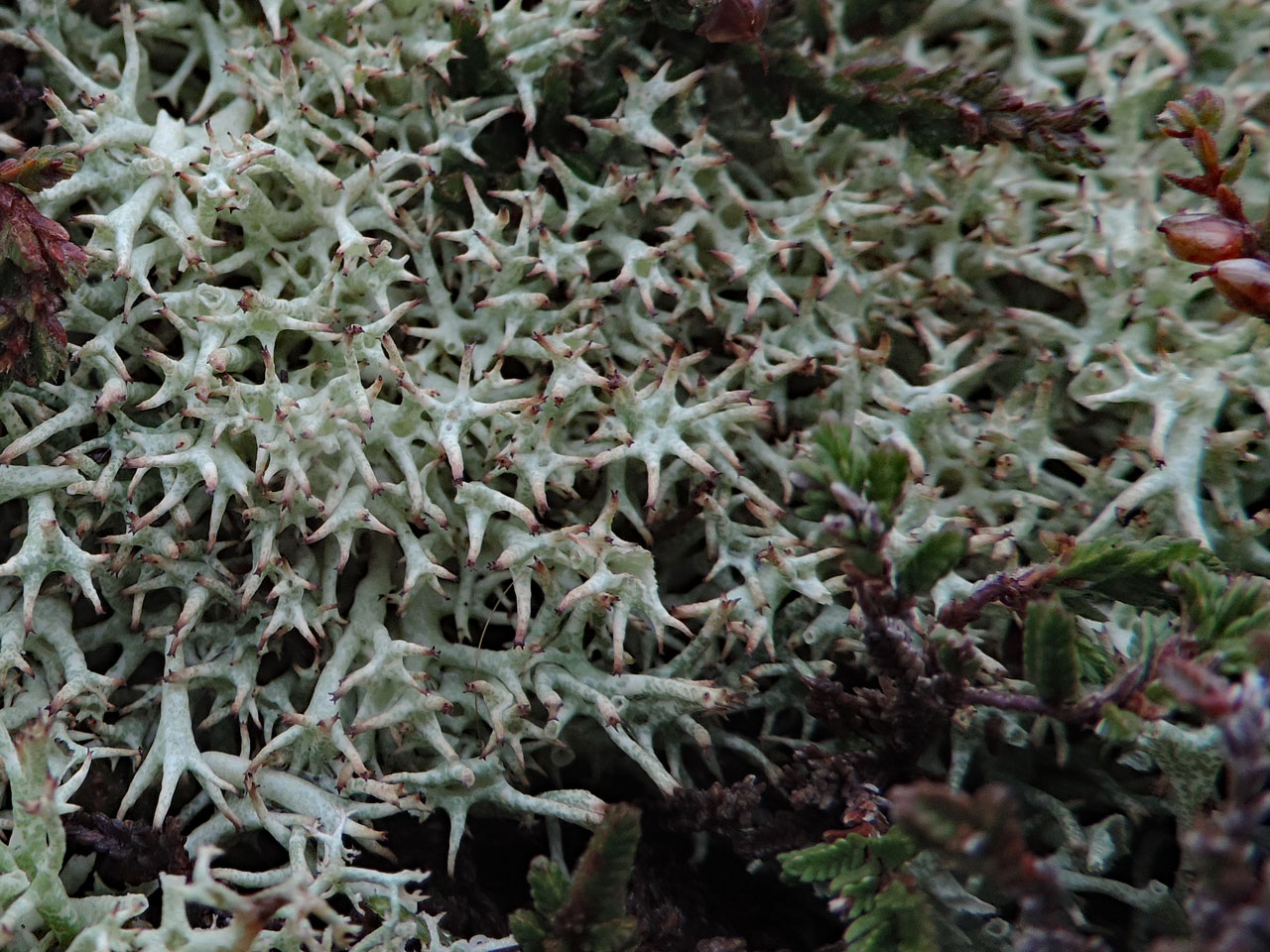
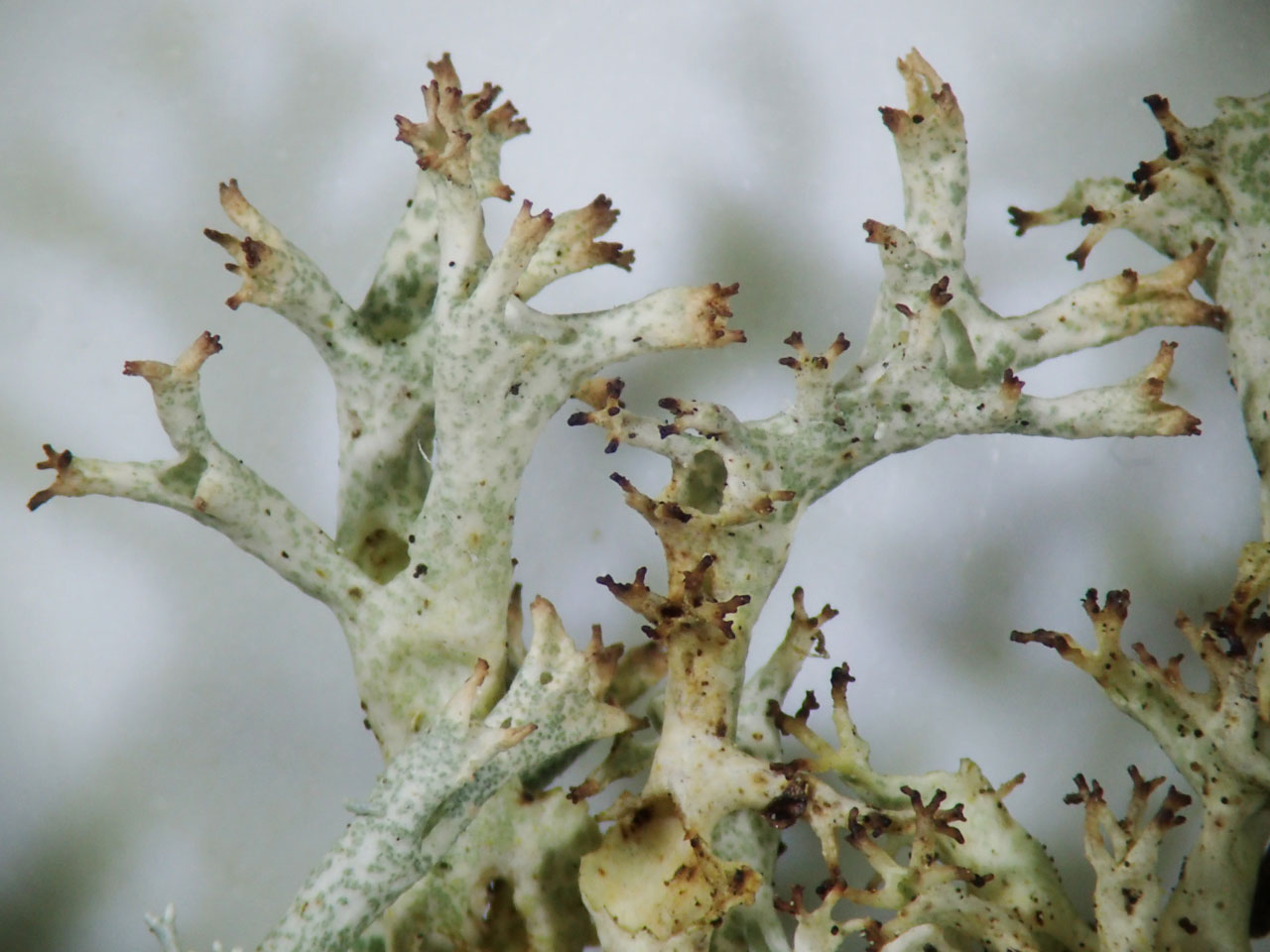
A large distinctive heaththorn Cladonia of low productivity well lit heaths, moors and acid grasslands. Distinguished by the yellow-green or greyish green sparsely branched, inflated and obviously hollow podetia along with the absence of squamules or soredia. The species is only easily confused with the uncommon C. zopfii, which see for the differences. More problematic is separating the two subspecies of C. uncialis subsp. uncialis and subsp. biuncialis. These have been demonstrated to have some genetic separation (Stenroos et al, 2015), but morphologically and chemically merge into each other. The genetic separation has not, however, been tested either in Britain or in areas where the two subspecies overlap. Subsp. uncialis tends to be markedly cushion-forming and predominantly tri- to tetra- or polychotomously branched giving the apices of the podetia a star-like appearance in crowded cushions. Squamatic acid is rarely present (UV–). Subsp. biuncialis tends not to form dense cushions but more loose decumbent mats and the podetia are regularly dichotomously and trichotomously branched. Squamatic acid (UV+) is usually present.
It is important to note that robust upright material of Subsp. biuncialis is not strictly dichotomous but, especially at the tips, can also branch into three and even fours, which makes separation of the subspecies more complicated than is sometimes assumed.
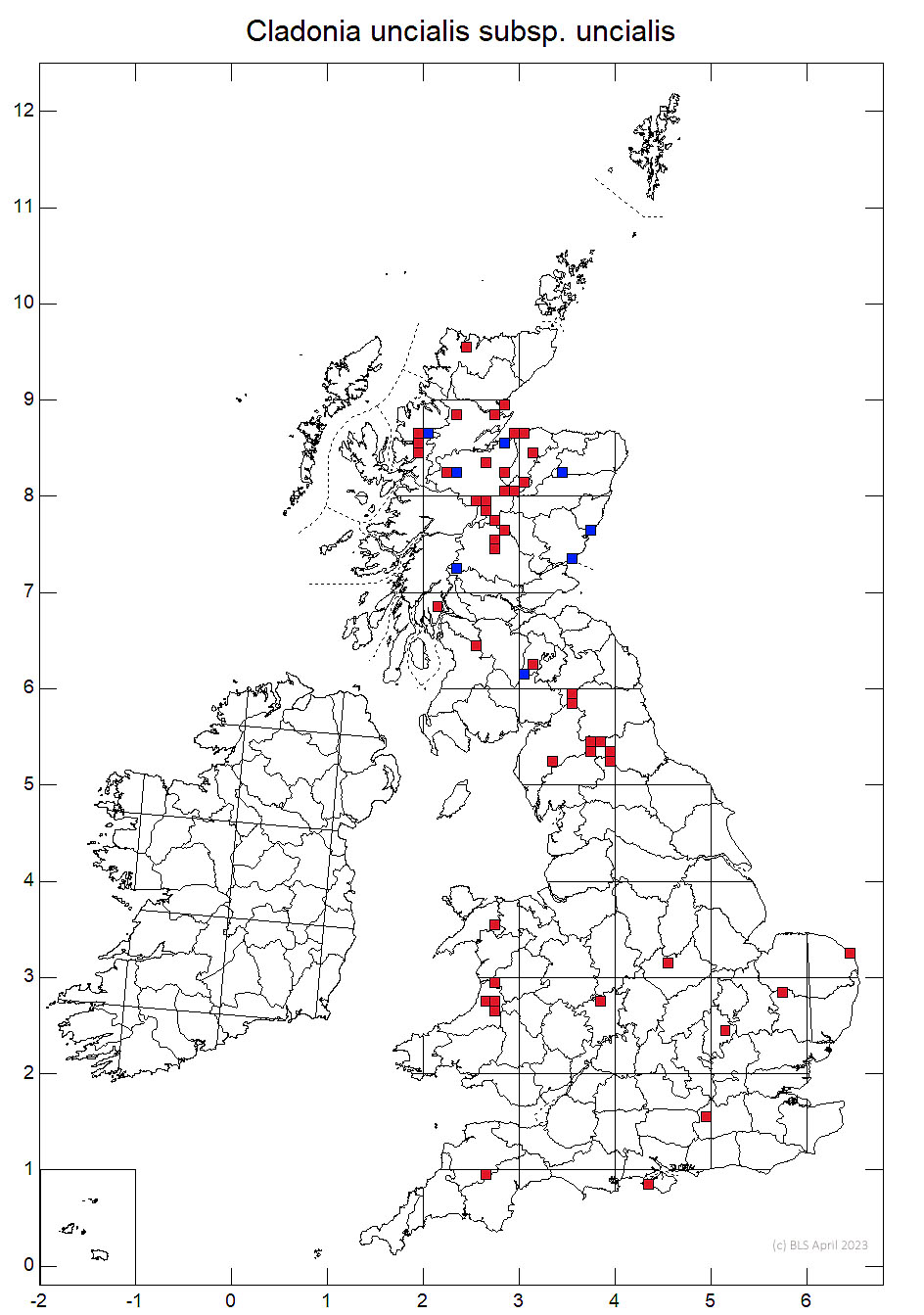
Cladonia uncialis subsp. uncialis is rather rare; principally found in E. Scotland, but with scattered records throughout Britain and Ireland, although some of the latter may be errors for robust Cladonia uncialis subsp. biuncialis.
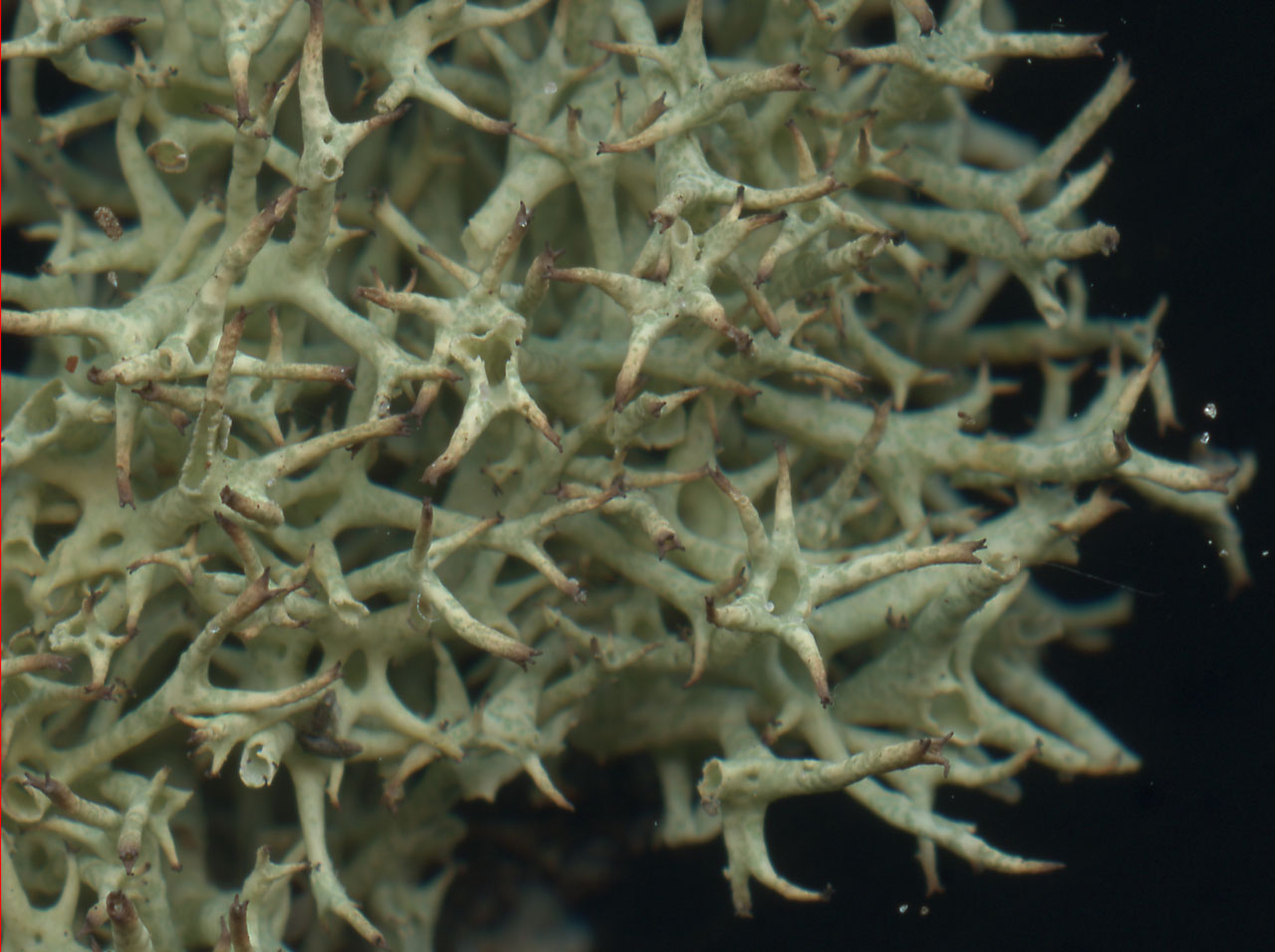
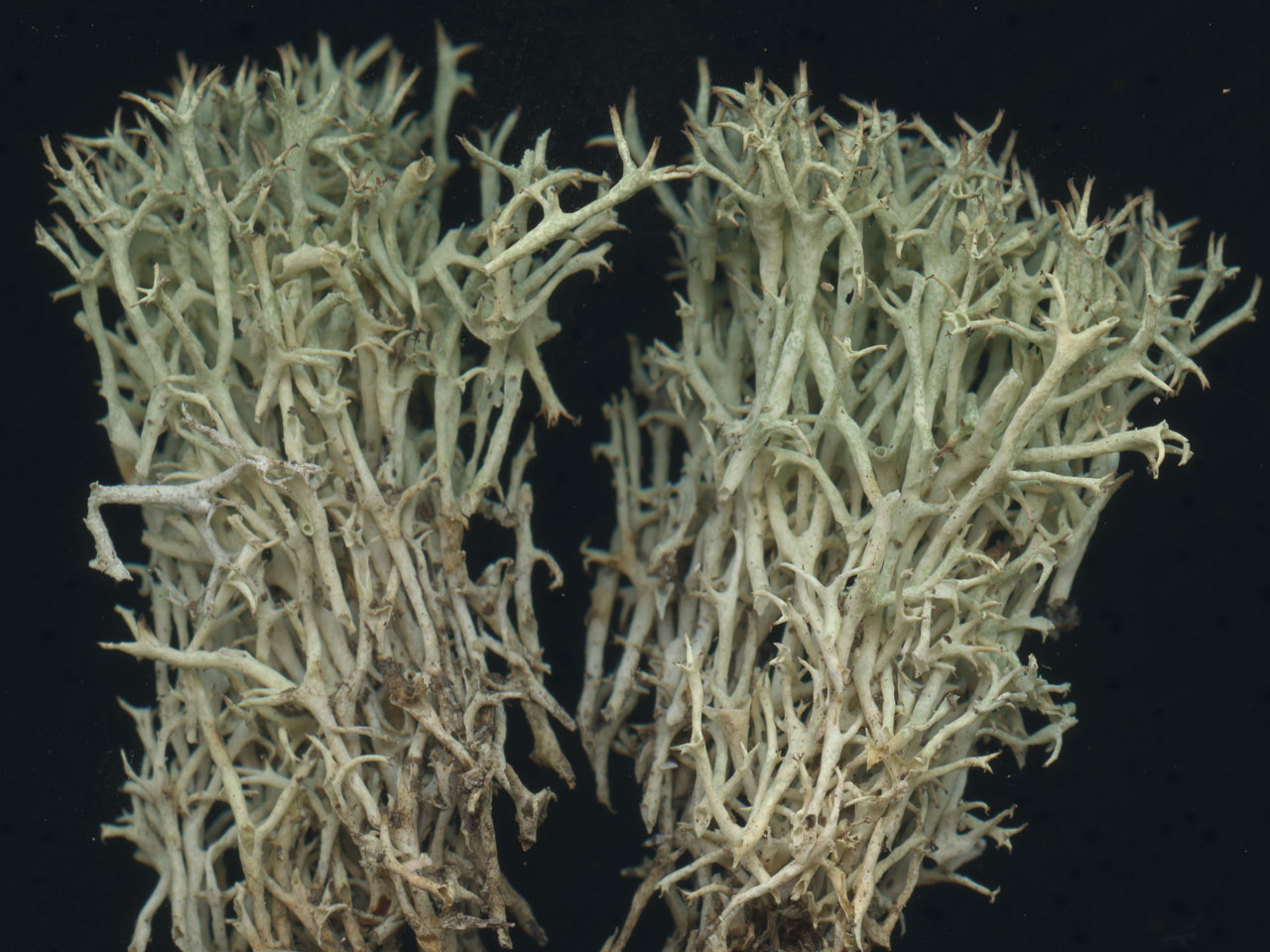
Podetia to 6 cm tall, without scyphi, yellow-green or greyish green, often brownish towards the abruptly pointed apices, forming ± compact, spiky tufts, the branching divergent, the axils mostly perforate, corticate throughout, the surface marbled in a ‘giraffe-skin’ pattern. Basal squamules absent. Apothecia and pycnidia brown, terminal. Thallus C–, K–, KC+ yellow, Pd–, medulla UV± white (usnic, ± squamatic acids, ± hypothamnolic acid). The UV fluorescence is only seen in the inside of the hollow podetia, so the podetia needs to be split to check this.
Two subspecies are recognised: subsp. uncialis and subsp. biuncialis. Stenroos et al. (2015) conducted a phylogenetic analysis of this aggregate, and concluded that the two morphs described above appear to be monophyletic, but that their distinction was insufficient to treat them unequivocally as separate species. They may be in a process of evolutionary divergence. See also C. zopfii.
Subsp. uncialis: podetia markedly cushion-forming, predominantly tri- to tetra- or polychotomously branched giving the apices of the podetia a star-like appearance; surface of central canal not powdery. Squamatic acid rarely present, so mainly UV–. Pycnidia and apothecia are more frequent in this subspecies.
On sand dunes, dry heathlands and montane heaths.

Rather rare; principally found in E. Scotland, but with scattered records throughout Britain and Ireland, although some of the latter may be errors for robust Cladonia uncialis subsp. biuncialis.
Britain: Near Threatened
Scotland: Priority Taxon for Biodiversity in Scotland
Pino-Bodas, R., Sanderson, N., Cannon, P., Aptroot, A., Coppins, B., Orange, A. & Simkin, J. (2021). Lecanorales: Cladoniaceae, including the genera Cladonia, Pilophorus and Pycnothelia. Revisions of British and Irish Lichens 19: 1-45. Link
Stenroos, S., Pino-Bodas, R., Weckman, D. & Ahti, T. (2015). Phylogeny of Cladonia uncialis (Cladoniaceae, Lecanoromycetes) and its allies. Lichenologist 47: 215–231.
Text by Neil A Sanderson, based on Pino-Bodas et al (2021)